Skills That Music Production Programs Teach You (And Jobs That They Prepare You For)
If you’ve ever listened to movie soundtracks on loop, or if you’ve ever wondered about how certain video game sound effects are created, music production programs might be tailor-made for you.
When you think of music production and sound design, you might think about composers like Mark Cofer first. But while some students do learn how to create music scores, the world of music production is so much bigger than that.
Can you imagine a horror movie without the sound of nails on chalkboard? What about a video game without battle cries or the clang of swords as they clash?
At its core, music production and sound design is about enhancing the emotional narrative of visual media. This involves the use of sound effects, sound mixing, sound editing, background music, and more. However, one person usually isn’t an expert in all of the above. Hence, as a student studying music production or sound design, you’ll have the opportunity to pick a specific area of focus.
It’s important to note that music production programs aren’t about producing music the same way that major celebrities and record labels produce music. Instead, you’re actually designing and making the music yourself.
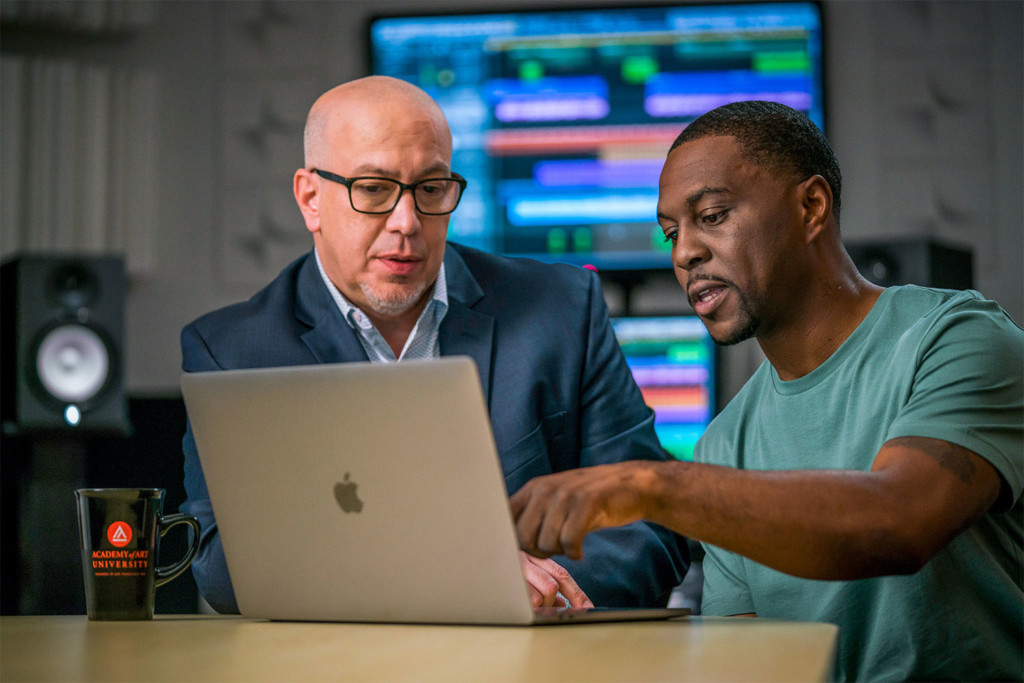

Building a Solid Base: Skills You’ll Learn in Music Production Programs
Since music production and sound design is such a broad field, not every person learns and uses the same skills.
For example, sound design students will need to know more about audio editing, mixing, and engineering than music scoring and composition students. On the other hand, student composers need to know more about music theory, music notation, how to write music for different kinds of visual media, and how to work with live and virtual orchestras.
Music production programs will also teach you how to:
- use professional audio processing, editing, and composing tools like Apple’s Logic Pro X
- match music and sound effects to what’s happening on-screen
- use music and sound effects libraries
- record good sound for live action film and edit out noise
- recognize basic musical elements just by hearing them
Of course, there are still common skills shared by most music production and sound design professionals, such as:
- how to tell a story through music or sound effects choices
- a familiarity with different production workflow processes in different industries, such as animation, live action, and video games.
Composing a Career: Job Options You’ll Enjoy After Graduating
Once you graduate with your music production or sound design degree, you’ll have many career paths to choose from. After all, we’re living in the age of visual media, and a lot of visual media requires musical accompaniment.
Some industries where you can build a future include:
- animation
- video games
- pop music and more
- live action feature film
- live action television
- radio
- theatre
- advertising and marketing
You can also find other applications for your skills, such as:
- teaching
- creating your own freelance business
- providing consulting services
But you might be wondering what your actual job title or position might be. Here are a few examples of what you could choose:
- sound mixer
- sound editor
- audio technician working with artists and producers
- studio manager who operates their own recording studio
- sound and music composer
- instrument tech or specialist
- digital audio editor for music, video, and film production
- foley artist
- music producer
- music supervisor for sourced music
- re-recording mixer for post-production work
- production recordist
Looking to expand your knowledge of music production and sound design? Request information about the School of Music Production & Sound Design at Academy of Art University.
On the other hand, if you’re ready to join our vibrant community of artists and designers, get started on your application today!