Animation vs VFX: Key Differences You’ll Learn in Animation School
Animation and visual effects (VFX) may lead you to career opportunities that fall on the same path. But still, make no mistake about it, there are stark differences between the two.
Animation and visual effects (VFX) are important parts of movies and other media. Knowing more about both can help you decide which career path to follow as you look into animation schools.
Animation
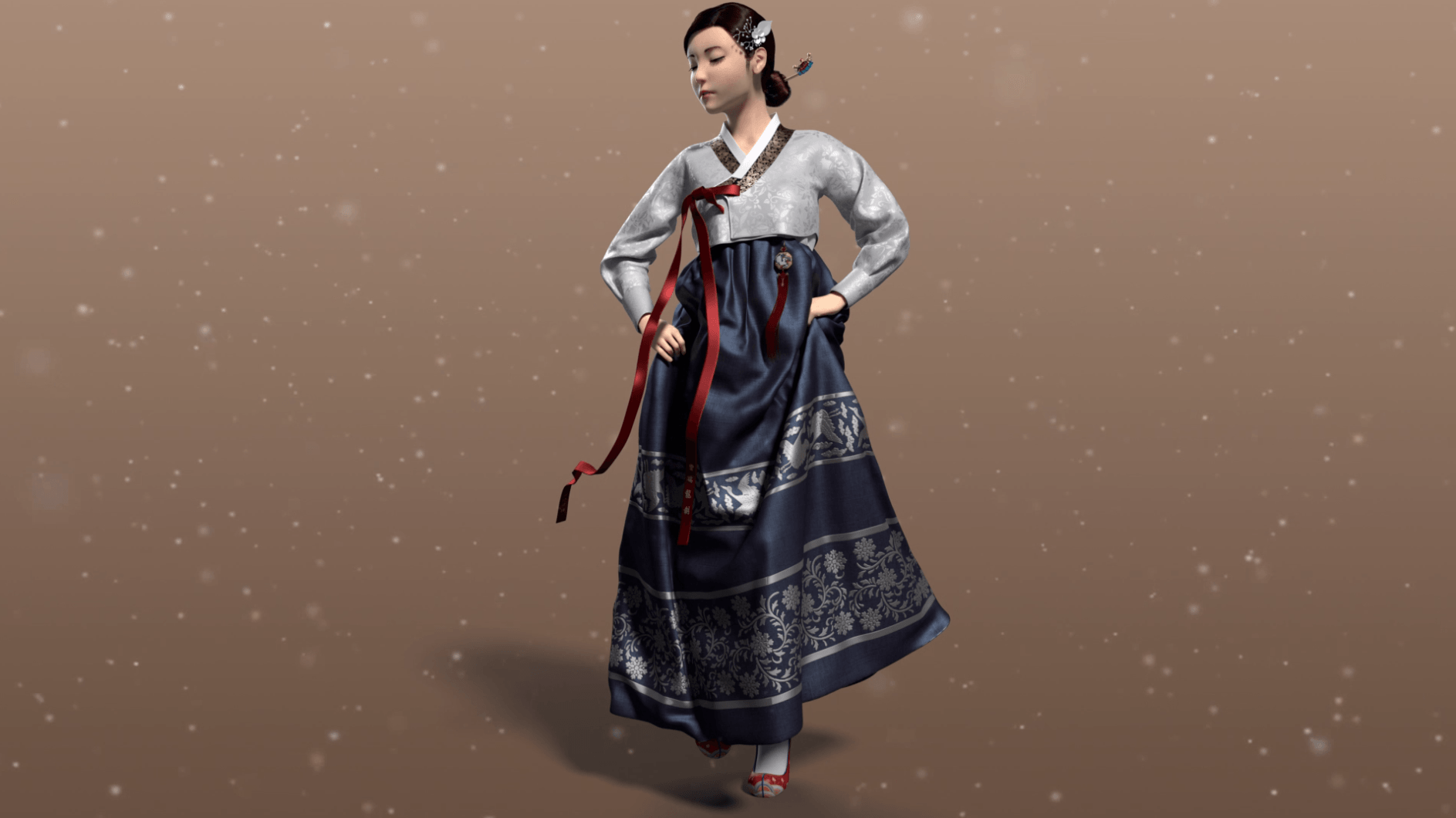
Animation involves using images to make it seem as though something is moving. Think of cartoons you’ve watched on TV or animated movies you’ve seen in theaters. The types of skills and tools you’ll need to use as an animator depends on the kind of animation you’re focusing on.
Different types of animation are used for media, including traditional, stop motion, and computer animation. Traditional animation involves drawing images on cells and moving them frame by frame. Stop motion involves using actual objects to make it look like they’re moving. Computer animation can refer to 2D or 3D animation.
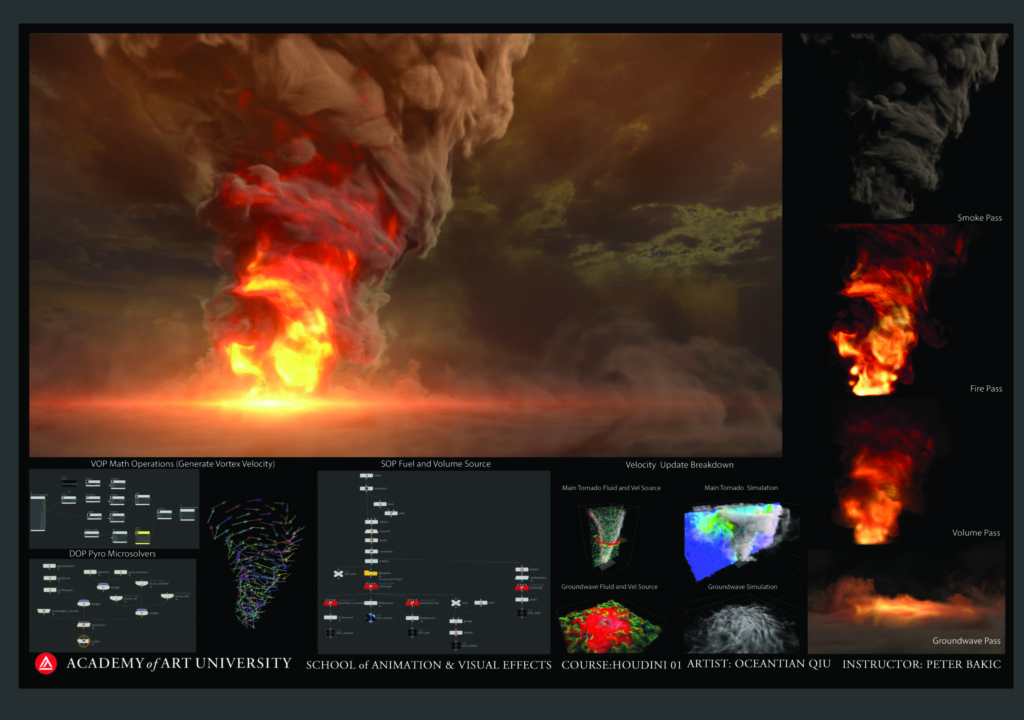
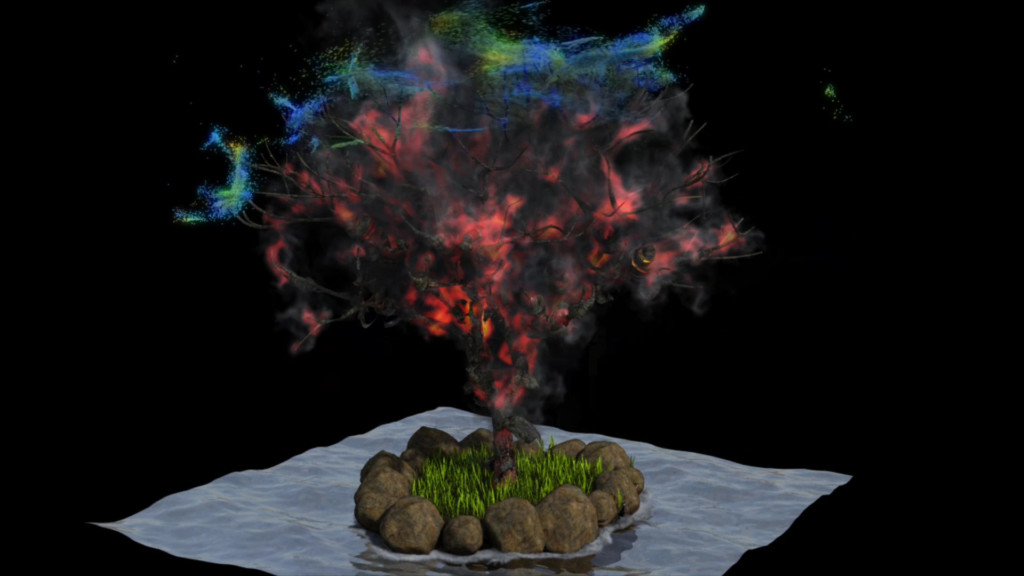
Visual Effects
Visual effects involves using different techniques and tools to create certain effects with live action footage. For example, VFX artists might use software to add a digital background to a movie scene.
Visual effects are usually done after filming is over and the post-production phase of filmmaking is under way. These artists have different ways of creating visual effects, such as matte painting, rotoscopy, compositing, and digital animation.
Career Opportunities
How do animation and VFX differ? Both of these involve working with media, but not the same exact type of media. With animation, you might work on cartoons or computer animated movies as part of your career. When you work with VFX, you’re using software, painting or other techniques to create certain effects for live action footage.
When you go to school for visual effects, VFX course options might include digital painting, rotoscoping, and principles of compositing. With animation, courses you might take include computer animation, traditional animation, or 3D character animation. The tools and techniques you end up learning for your career will vary based on your area of interest, such as 3D animation or digital animation for visual effects.


The career opportunities that are available depend on which one you prefer to focus on. Examples of careers in animation include the following:
- rigging artists
- 2D animators
- 3D animators
- 3D modelers


With visual effects, possible careers include:
- matte painters
- rotoscope artists
- 3D match moving
- paint artists

Salary and Job Growth
In terms of salary and job growth, animators and visual effects artists are very similar. Both make an average salary that’s in the same range, and the job outlook for both is expected to move along at a steady pace over the next several years. The median salary for animators is roughly $72,000, while the median salary for visual effects artists is roughly $70,000.
Each has their own advantages over the other. Whichever specialization you choose, though, what’s important is that you are pursuing the career that will fulfill your true creative passion.
Apply now for Academy of Art University’s School of Animation & Visual Effects program if you’re ready to start on your career industry. Request for more information from our admissions representatives if you still need to clarify some details.
Header image courtesy of School of Animation & Visual Effects student Seo Ryong Jaw.